Mode 5: Multi-Modal Components
Definition
This mode is typically applied when the LLM alone cannot handle the task. It requires additional multi-modal components to process audio, images, or videos, or to convert the LLM-generated responses into other modalities, such as voice or images. This is commonly needed in both the planning and generation stages.
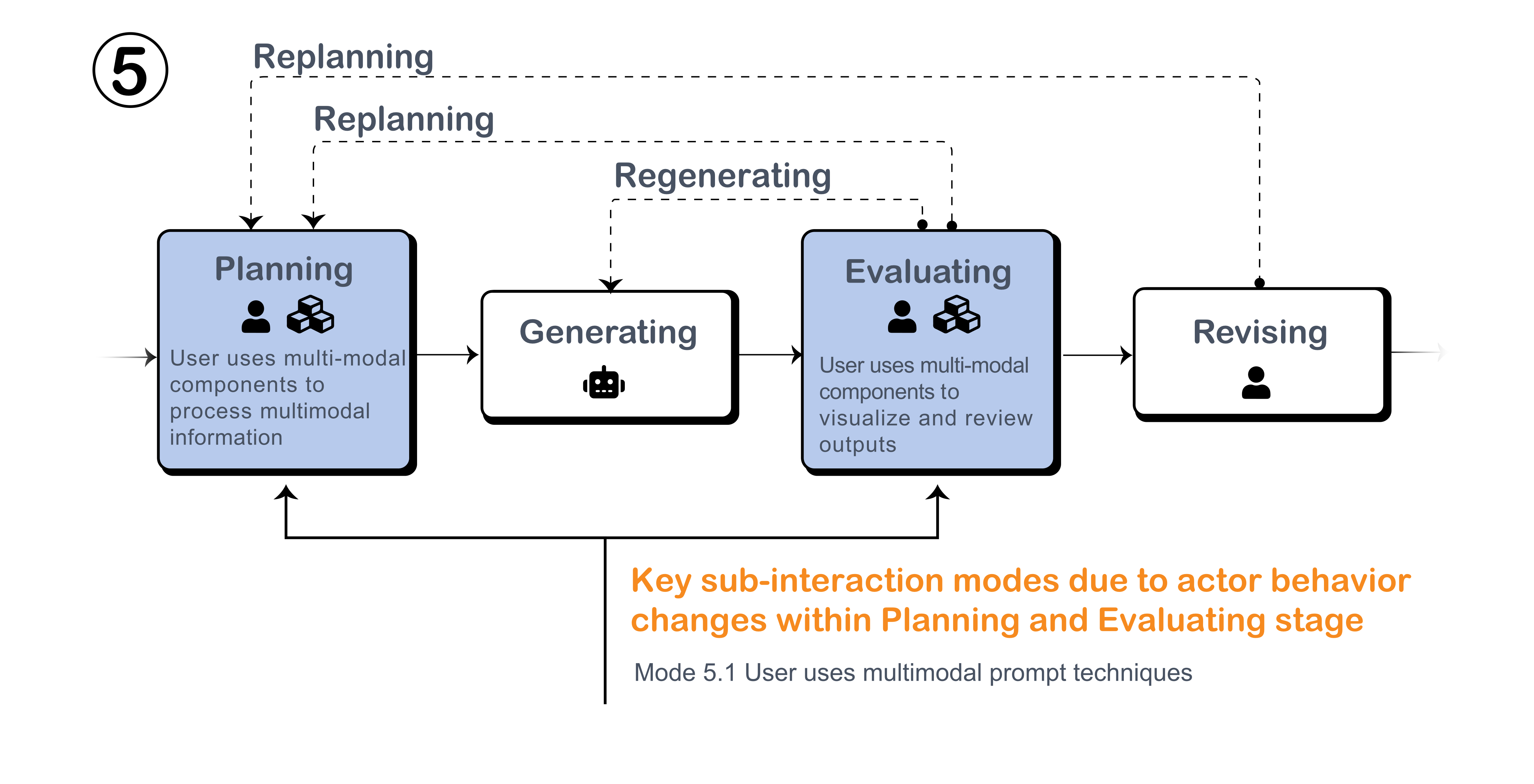
Figure: Multi-modal components facilitate tasks during Planning and Evaluating stages.
Key Interaction Modes and Examples
Multi-modal components prompting techniques.
-
Role play. The user can ask LLM-system to generate responses from persona perspectives based on users' inputs to facilitate discussion.
-
Actively asking intention. Users provide instructions to the LLM, which then executes a multimodal task, such as constructing architecture in a 3D environment, while actively prompting the user to clarify any ambiguities in the instructions. The system developed to probe multiple options for users, actively ask questions about users' information, styles and vibes to enrich the prompt. And a wearable augmented reality tool to proactively ask questions based on users’ gaze and voice, and then generate summarizations and blogs based on users’ answer. By incorporating these clarifications, the LLM enhances its execution accuracy and avoids repeating errors previously corrected through user input.
User uses LLM with multimodal input and (or) output components.
In many situations, another modality could be unavailable, augmenting the LLM with extra multi-modal components could be useful. For example, converting videos’ voice to text transcripts, and inputting it to LLM so that LLM can create further analysis, provide concepts summarization, generate questions answering pairs. Etc. LLMs can be adapted to process queries incorporating non-textual elements, expanding their capabilities across various media types. For example, Gardner et al. combined music features, such as beats, rhythms, and chords, with text prompts to create multi-modal inputs for human-formed LLMs. This framework facilitates music analysis tasks, such as generating detailed descriptions for a piece of music or reasoning tasks like re-creating compositions, with results provided in text format. Multi-modal capabilities also support video transformation, where video inputs are converted into structured outputs, such as text summaries, object relationship graphs, or other organized formats, or are converted into embeddings and used in combination with text to generate video or audio outputs. Additionally, multi-modal enhancements improve usage search functionality by enabling LLMs to generate captions and alt-text for images and to compare similarities between images and user queries for quicker retrievals.